本 Notebook 概述#
模块化构建块的激励性示例
连接距离、对齐器、分类器
成对 transformer - 时间序列距离和核的“类型”
时间序列对齐和对齐距离,例如时间规整
距离、核、对齐器的组合模式
[1]:
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
6.1 激励性示例#
对象类型之间丰富的组件关系!
许多分类器、回归器、聚类器使用距离或核
距离和核通常是复合的,例如,距离之和、独立距离
时间序列距离通常基于标量多变量距离(例如,欧氏距离)
时间序列距离通常基于对齐,时间序列对齐器是一种评估器类型!
对齐器内部通常使用标量单/多变量距离
示例
使用
sklearn最近邻的 1-NN使用来自
dtw-python库的多变量动态时间规整距离基于来自
scipy的多变量"mahalanobis"距离在
sktime兼容接口中,由自定义组件构建
因此,从概念上讲
我们使用
scipyMahalanobis 距离构建序列对齐算法(dtw-python)我们从对齐算法中获得距离矩阵计算
我们在
sklearnknn 中使用该距离矩阵结合起来,这就是一个时间序列分类器!
[2]:
from sktime.alignment.dtw_python import AlignerDTWfromDist
from sktime.classification.distance_based import KNeighborsTimeSeriesClassifier
from sktime.dists_kernels.compose_from_align import DistFromAligner
from sktime.dists_kernels.scipy_dist import ScipyDist
# Mahalanobis distance on R^n
mahalanobis_dist = ScipyDist(metric="mahalanobis") # uses scipy distances
# pairwise multivariate aligner from dtw-python with Mahalanobis distance
mw_aligner = AlignerDTWfromDist(mahalanobis_dist) # uses dtw-python
# turning this into alignment distance on time series
dtw_dist = DistFromAligner(mw_aligner) # interface mutation to distance
# and using this distance in a k-nn classifier
clf = KNeighborsTimeSeriesClassifier(distance=dtw_dist) # uses sklearn knn
[3]:
clf.get_params()
[3]:
{'algorithm': 'brute',
'distance': DistFromAligner(aligner=AlignerDTWfromDist(dist_trafo=ScipyDist(metric='mahalanobis'))),
'distance_mtype': None,
'distance_params': None,
'leaf_size': 30,
'n_jobs': None,
'n_neighbors': 1,
'pass_train_distances': False,
'weights': 'uniform',
'distance__aligner': AlignerDTWfromDist(dist_trafo=ScipyDist(metric='mahalanobis')),
'distance__aligner__dist_trafo': ScipyDist(metric='mahalanobis'),
'distance__aligner__open_begin': False,
'distance__aligner__open_end': False,
'distance__aligner__step_pattern': 'symmetric2',
'distance__aligner__window_type': 'none',
'distance__aligner__dist_trafo__colalign': 'intersect',
'distance__aligner__dist_trafo__metric': 'mahalanobis',
'distance__aligner__dist_trafo__metric_kwargs': None,
'distance__aligner__dist_trafo__p': 2,
'distance__aligner__dist_trafo__var_weights': None}
这个链条中的所有对象是什么?
ScipyDist- 标量之间的成对距离 -transformer-pairwise类型AlignerDtwFromDist- 时间序列对齐算法 -aligner类型DistFromAligner- 时间序列之间的成对距离 -transformer-pairwise-panel类型KNeighborsTimeSeriesClassifier- 时间序列分类器
[4]:
from sktime.registry import scitype
scitype(mw_aligner) # prints the type of estimator (as a string)
# same for other components
[4]:
'aligner'
让我们过一遍这些 - 我们已经看过分类器了。
6.2 时间序列距离和核 - 成对面板 transformer#
6.2.1 距离、核 - 通用接口#
成对面板 transformer 为面板中的每对序列生成一个距离
[5]:
from sktime.datasets import load_osuleaf
# load an example time series panel in numpy mtype
X, _ = load_osuleaf(return_type="numpy3D")
X1 = X[:3]
X2 = X[5:10]
[6]:
# constructing the transformer
from sktime.dists_kernels import FlatDist
from sktime.dists_kernels.scipy_dist import ScipyDist
# paired Euclidean distances, over time points
eucl_dist = FlatDist(ScipyDist())
[7]:
X1.shape
[7]:
(3, 1, 427)
[8]:
X2.shape
[8]:
(5, 1, 427)
X1 是包含 3 个序列的面板,X2 是包含 5 个序列的面板
因此,从 X1 到 X2 的成对距离矩阵应具有形状 (3, 5)
[9]:
distmat = eucl_dist(X1, X2)
# alternatively, via the transform method
distmat = eucl_dist.transform(X1, X2)
distmat
[9]:
array([[29.94033435, 30.69443315, 29.02704475, 30.49413394, 29.77534229],
[28.86289916, 32.03165025, 29.6118973 , 32.95499251, 30.82017584],
[29.52672336, 18.76259726, 30.55213501, 15.93324954, 27.89072122]])
[10]:
distmat.shape
[10]:
(3, 5)
使用单个参数调用或 transform 与传递两次相同
[11]:
distmat_symm = eucl_dist.transform(X1)
distmat_symm
[11]:
array([[ 0. , 24.58470308, 33.83913255],
[24.58470308, 0. , 35.44109497],
[33.83913255, 35.44109497, 0. ]])
成对面板 transformer 与 scikit-learn / scikit-base 接口兼容且可组合,就像 sktime 中的其他所有内容一样
[12]:
eucl_dist.get_params()
[12]:
{'transformer': ScipyDist(),
'transformer__colalign': 'intersect',
'transformer__metric': 'euclidean',
'transformer__metric_kwargs': None,
'transformer__p': 2,
'transformer__var_weights': None}
6.2.2 时间序列距离、核 - 组合#
成对 transformer 可以通过多种方式组合
算术运算,例如加法、乘法 - 使用 dunder
+、*等,或CombinedDistance子集到一个或多个列 - 使用
my_dist[colnames]dunder在多变量面板中对单变量距离进行求和或聚合,使用
IndepDist(也称为“独立距离”)与序列到序列 transformer 组合 - 使用
*dunder 或make_pipeline
[13]:
from sktime.datasets import load_basic_motions
# load an example time series panel in numpy mtype
X, _ = load_basic_motions(return_type="numpy3D")
X = X[:3]
X.shape
[13]:
(3, 6, 100)
[14]:
# example 1: variable subsetting and arithmetic combinations
# we define *two* distances now
from sktime.dists_kernels import FlatDist, ScipyDist
# Euclidean distance (on flattened time series)
eucl_dist = FlatDist(ScipyDist())
# Mahalanobis distance (on flattened time series)
cos_dist = FlatDist(ScipyDist(metric="cosine"))
# arithmetic product of:
# * the Euclidean distance on gyrometer 2 time series
# * the Cosine distance on accelerometer 3 time series
prod_dist_42 = eucl_dist[4] * cos_dist[2]
prod_dist_42
[14]:
CombinedDistance(operation='*',
pw_trafos=[PwTrafoPanelPipeline(pw_trafo=FlatDist(transformer=ScipyDist()),
transformers=[ColumnSelect(columns=4)]),
PwTrafoPanelPipeline(pw_trafo=FlatDist(transformer=ScipyDist(metric='cosine')),
transformers=[ColumnSelect(columns=2)])])请重新运行此单元格以显示 HTML 表示或信任此 Notebook。CombinedDistance(operation='*',
pw_trafos=[PwTrafoPanelPipeline(pw_trafo=FlatDist(transformer=ScipyDist()),
transformers=[ColumnSelect(columns=4)]),
PwTrafoPanelPipeline(pw_trafo=FlatDist(transformer=ScipyDist(metric='cosine')),
transformers=[ColumnSelect(columns=2)])])ScipyDist()
ColumnSelect(columns=4)
ScipyDist(metric='cosine')
ColumnSelect(columns=2)
[15]:
prod_dist_42(X)
[15]:
array([[0. , 1.87274896, 2.28712525],
[1.87274896, 0. , 2.62764453],
[2.28712525, 2.62764453, 0. ]])
[16]:
# example 2: independent dynamic time warping distance
from sktime.alignment.dtw_python import AlignerDTW
from sktime.dists_kernels.compose_from_align import DistFromAligner
from sktime.dists_kernels.indep import IndepDist
# dynamic time warping distance - this is multivariate
dtw_dist = DistFromAligner(AlignerDTW())
# independent distance - by default IndepDist sums over univariate distances
indep_dtw_dist = IndepDist(dtw_dist)
# that is, this distance is arithmetic sum of
# * DTW distance on accelerometer 1 time series
# * DTW distance on accelerometer 2 time series
# * DTW distance on accelerometer 3 time series
# * DTW distance on gyrometer 1 time series
# * DTW distance on gyrometer 2 time series
# * DTW distance on gyrometer 3 time series
[17]:
indep_dtw_dist(X)
[17]:
array([[ 0. , 31.7765985 , 32.65822 ],
[31.7765985 , 0. , 39.78652033],
[32.65822 , 39.78652033, 0. ]])
[18]:
# example 3: dynamic time warping distance on first differences
from sktime.transformations.series.difference import Differencer
diff_dtw_distance = Differencer() * dtw_dist
[19]:
diff_dtw_distance(X)
[19]:
array([[ 0. , 20.622806, 27.731956],
[20.622806, 0. , 30.487498],
[27.731956, 30.487498, 0. ]])
一些组合可以作为基于高效 numba 的距离使用。
例如,差分然后 DTW 可作为 sktime.dists_kernels.dtw 中“固定”的 sktime 本地实现 DtwDist(derivative=True) 使用。
6.3 成对表格 transformer#
6.3.1 成对表格 transformer - 通用接口#
成对表格 transformer 转换成对的普通表格数据,例如普通 pd.DataFrame
为每对行生成一个距离
[20]:
from sktime.datatypes import get_examples
# we retrieve some DataFrame examples
X_tabular = get_examples("pd.DataFrame", "Series")[1]
X2_tabular = get_examples("pd.DataFrame", "Series")[1][0:3]
[21]:
# just an ordinary DataFrame, no time series
X_tabular
[21]:
| a | b | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.0 | 3.000000 |
| 1 | 4.0 | 7.000000 |
| 2 | 0.5 | 2.000000 |
| 3 | -3.0 | -0.428571 |
[22]:
X2_tabular
[22]:
| a | b | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.0 | 3.0 |
| 1 | 4.0 | 7.0 |
| 2 | 0.5 | 2.0 |
示例:行之间的成对欧氏距离
[23]:
# constructing the transformer
from sktime.dists_kernels import ScipyDist
# mean of paired Euclidean distances
my_tabular_dist = ScipyDist(metric="euclidean")
[24]:
# obtain matrix of distances between each pair of rows in X_tabular, X2_tabular
my_tabular_dist(X_tabular, X2_tabular)
[24]:
array([[ 0. , 5. , 1.11803399],
[ 5. , 0. , 6.10327781],
[ 1.11803399, 6.10327781, 0. ],
[ 5.26831112, 10.20704039, 4.26004216]])
[25]:
# alternative call with transform:
my_tabular_dist.transform(X_tabular, X2_tabular)
[25]:
array([[ 0. , 5. , 1.11803399],
[ 5. , 0. , 6.10327781],
[ 1.11803399, 6.10327781, 0. ],
[ 5.26831112, 10.20704039, 4.26004216]])
[26]:
# as with pairwise panel transformers, one arg means second is the same
my_tabular_dist(X_tabular)
[26]:
array([[ 0. , 5. , 1.11803399, 5.26831112],
[ 5. , 0. , 6.10327781, 10.20704039],
[ 1.11803399, 6.10327781, 0. , 4.26004216],
[ 5.26831112, 10.20704039, 4.26004216, 0. ]])
6.3.2 从表格 transformer 构建成对时间序列 transformer#
“简单”时间序列距离可以直接从表格 transformer 中获得
将时间序列展平为表格,然后计算距离 -
FlatDist聚合表格距离矩阵,来自两个单独的时间序列 -
AggrDist
这些是重要的“基线”距离!
两者都可用于 sktime 成对 transformer 和 sklearn 成对 transformer。
这些类被称为“dist”,但都适用于核。
[27]:
from sktime.datasets import load_basic_motions
# load an example time series panel in numpy mtype
X, _ = load_basic_motions(return_type="numpy3D")
X = X[:3]
X.shape
[27]:
(3, 6, 100)
[28]:
# example 1: flat Gaussian RBF kernel between time series
from sklearn.gaussian_process.kernels import RBF
from sktime.dists_kernels import FlatDist
flat_gaussian_tskernel = FlatDist(RBF(length_scale=10))
flat_gaussian_tskernel.get_params()
[28]:
{'transformer': RBF(length_scale=10),
'transformer__length_scale': 10,
'transformer__length_scale_bounds': (1e-05, 100000.0)}
[29]:
flat_gaussian_tskernel(X)
[29]:
array([[1. , 0.02267939, 0.28034066],
[0.02267939, 1. , 0.05447445],
[0.28034066, 0.05447445, 1. ]])
[30]:
# example 2: pairwise cosine distance - we've already seen FlatDist a couple times
from sktime.dists_kernels import FlatDist, ScipyDist
cos_tsdist = FlatDist(ScipyDist(metric="cosine"))
cos_tsdist.get_params()
[30]:
{'transformer': ScipyDist(metric='cosine'),
'transformer__colalign': 'intersect',
'transformer__metric': 'cosine',
'transformer__metric_kwargs': None,
'transformer__p': 2,
'transformer__var_weights': None}
[31]:
cos_tsdist(X)
[31]:
array([[1.11022302e-16, 1.36699314e+00, 6.99338545e-01],
[1.36699314e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 1.10061843e+00],
[6.99338545e-01, 1.10061843e+00, 0.00000000e+00]])
6.4 对齐算法,也称为对齐器#
“对齐器”为 2 个或更多时间序列找到一个新的索引集,使它们变得“相似”
新的索引集是对旧索引集的非线性重参数化
通常,对齐器还会产生两个序列之间的总体距离
6.4.1 对齐器 - 通用接口#
对齐器方法
fit- 计算对齐get_alignment- 返回重新参数化的索引,也称为“对齐路径”get_aligned返回重新参数化的序列get_distance返回两个对齐序列之间的距离 - 仅当"capability:get_distance"可用时
让我们尝试对齐 OSUleaf 中的两个叶子轮廓!
OSUleaf 是一个包含展平树叶子轮廓的面板数据集
实例 = 叶子
索引(“时间”)= 距质心的角度
变量 = 在该角度下轮廓线与质心的距离
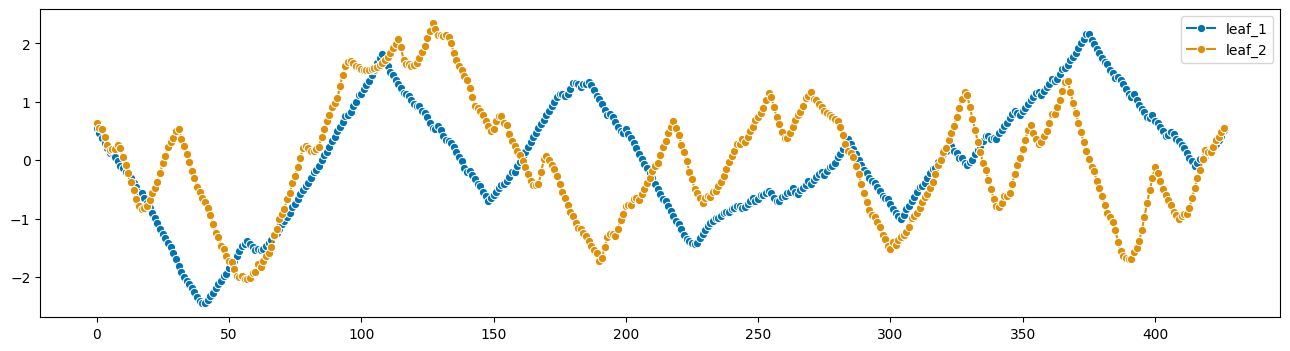
[32]:
from sktime.datasets import load_osuleaf
# load an example time series panel in numpy mtype
X, _ = load_osuleaf(return_type="pd-multiindex")
X1 = X.loc[0] # leaf 0
X2 = X.loc[1] # leaf 1
[33]:
from sktime.utils.plotting import plot_series
plot_series(X1, X2, labels=["leaf_1", "leaf_2"])
[33]:
(<Figure size 1600x400 with 1 Axes>, <Axes: >)
[34]:
from sktime.alignment.dtw_python import AlignerDTW
# use dtw-python package for aligning
# simple univariate alignment algorithm with default params
aligner = AlignerDTW()
[35]:
aligner.fit([X1, X2]) # series to align need to be passed as list
[35]:
AlignerDTW()请重新运行此单元格以显示 HTML 表示或信任此 Notebook。
AlignerDTW()
[36]:
# alignment path
aligner.get_alignment()
# this aligns, e.g.:
# from row "2": aligns index 0 in X1 with index 2 of X2
# from row "664": aligns index 424 in X1 with index 423 of X2
[36]:
| ind0 | ind1 | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 |
| 4 | 2 | 3 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 663 | 423 | 422 |
| 664 | 424 | 423 |
| 665 | 425 | 424 |
| 666 | 426 | 425 |
| 667 | 426 | 426 |
668 行 × 2 列
[37]:
# obtain the aligned versions of the two series
X1_al, X2_al = aligner.get_aligned()
[38]:
from sktime.utils.plotting import plot_series
plot_series(
X1_al.reset_index(drop=True),
X2_al.reset_index(drop=True),
labels=["leaf_1", "leaf_2"],
)
[38]:
(<Figure size 1600x400 with 1 Axes>, <Axes: >)
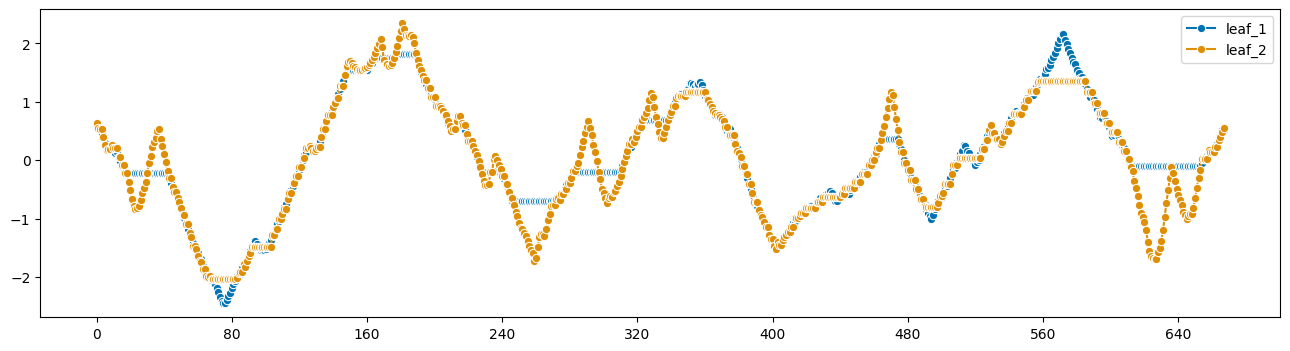
DTW 对齐器实现了“距离”
直观地说,它是在对齐后对距离求和,以及拉伸量的距离
[39]:
# the AlignerDTW class (based on dtw-python) doesn't just align
# it also produces a distance
aligner.get_tags()
[39]:
{'python_dependencies_alias': {'dtw-python': 'dtw'},
'capability:multiple-alignment': False,
'capability:distance': True,
'capability:distance-matrix': True,
'python_dependencies': 'dtw-python'}
[40]:
# this is the distance between the two time series we aligned
aligner.get_distance()
[40]:
113.73231668301005
6.4.2 基于对齐的时间序列距离#
DistFromAligner 包装器简单地计算每对对齐序列的距离。
这将任何对齐器转换为时间序列距离
[41]:
from sktime.alignment.dtw_python import AlignerDTW
from sktime.dists_kernels.compose_from_align import DistFromAligner
# dynamic time warping distance - this is multivariate
dtw_dist = DistFromAligner(AlignerDTW())
[42]:
from sktime.datasets import load_osuleaf
# load an example time series panel in numpy mtype
X, _ = load_osuleaf(return_type="numpy3D")
X1 = X[:3]
X2 = X[5:10]
[43]:
dtw_distmat = dtw_dist(X1, X2)
dtw_distmat
[43]:
array([[165.25420136, 148.53521913, 159.93034065, 158.50379563,
155.98824527],
[153.5587322 , 151.52004769, 125.14570395, 183.97186106,
93.55389512],
[170.41354799, 154.24275848, 212.54601605, 66.59572457,
295.32544676]])
[44]:
dtw_distmat.shape
[44]:
(3, 5)
6.5 回顾最初的示例#
[45]:
from sktime.alignment.dtw_python import AlignerDTWfromDist
from sktime.classification.distance_based import KNeighborsTimeSeriesClassifier
from sktime.dists_kernels.compose_from_align import DistFromAligner
from sktime.dists_kernels.scipy_dist import ScipyDist
# Mahalanobis distance on R^n
mahalanobis_dist = ScipyDist(metric="mahalanobis") # uses scipy distances
# pairwise multivariate aligner from dtw-python with Mahalanobis distance
mw_aligner = AlignerDTWfromDist(mahalanobis_dist) # uses dtw-python
# turning this into alignment distance on time series
dtw_dist = DistFromAligner(mw_aligner) # interface mutation to distance
# and using this distance in a k-nn classifier
clf = KNeighborsTimeSeriesClassifier(distance=dtw_dist) # uses sklearn knn
[46]:
clf
[46]:
KNeighborsTimeSeriesClassifier(distance=DistFromAligner(aligner=AlignerDTWfromDist(dist_trafo=ScipyDist(metric='mahalanobis'))))请重新运行此单元格以显示 HTML 表示或信任此 Notebook。
KNeighborsTimeSeriesClassifier(distance=DistFromAligner(aligner=AlignerDTWfromDist(dist_trafo=ScipyDist(metric='mahalanobis'))))
ScipyDist(metric='mahalanobis')
我们使用
scipyMahalanobis 距离构建序列对齐算法(dtw-python)我们从对齐算法中获得距离矩阵计算
我们在
sklearnknn 中使用该距离矩阵结合起来,这就是一个时间序列分类器!
6.6 搜索距离、核、transformer#
与所有 sktime 对象一样,我们可以使用 registry.all_estimators 工具显示 sktime 中的所有 transformer。
相关的科学类型有
"transformer-pairwise"用于表格数据上的所有成对 transformer"transformer-panel"用于面板数据上的所有成对 transformer"aligner"用于所有时间序列对齐器"transformer"用于所有 transformer,这些 transformer 可以与上述所有类型组合
[47]:
from sktime.registry import all_estimators
[48]:
# listing all pairwise panel transformers - distances, kernels on time series
all_estimators("transformer-pairwise-panel", as_dataframe=True)
[48]:
| 名称 | 对象 | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | AggrDist | <class 'sktime.dists_kernels.compose_tab_to_pa...' |
| 1 | CombinedDistance | <class 'sktime.dists_kernels.algebra.CombinedD...' |
| 2 | ConstantPwTrafoPanel | <class 'sktime.dists_kernels.dummy.ConstantPwT...' |
| 3 | DistFromAligner | <class 'sktime.dists_kernels.compose_from_alig...' |
| 4 | DistFromKernel | <class 'sktime.dists_kernels.dist_to_kern.Dist...' |
| 5 | DtwDist | <class 'sktime.dists_kernels.dtw.DtwDist'> |
| 6 | EditDist | <class 'sktime.dists_kernels.edit_dist.EditDist'> |
| 7 | FlatDist | <class 'sktime.dists_kernels.compose_tab_to_pa...' |
| 8 | IndepDist | <class 'sktime.dists_kernels.indep.IndepDist'> |
| 9 | KernelFromDist | <class 'sktime.dists_kernels.dist_to_kern.Kern...' |
| 10 | PwTrafoPanelPipeline | <class 'sktime.dists_kernels.compose.PwTrafoPa...' |
| 11 | SignatureKernel | <class 'sktime.dists_kernels.signature_kernel.... |
[49]:
# listing all pairwise (tabular) transformers - distances, kernels on vectors/df-rows
all_estimators("transformer-pairwise", as_dataframe=True)
[49]:
| 名称 | 对象 | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | ScipyDist | <class 'sktime.dists_kernels.scipy_dist.ScipyD...' |
[50]:
# listing all alignment algorithms that can produce distances
all_estimators("aligner", as_dataframe=True, filter_tags={"capability:distance": True})
[50]:
| 名称 | 对象 | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | AlignerDTW | <class 'sktime.alignment.dtw_python.AlignerDTW'> |
| 1 | AlignerDTWfromDist | <class 'sktime.alignment.dtw_python.AlignerDTW...' |
| 2 | AlignerDtwNumba | <class 'sktime.alignment.dtw_numba.AlignerDtwN...' |
6.7 展望、路线图 - 面板任务#
实现评估器 - 距离、分类器等
后端优化 -
numba, 分布式/并行序列到序列回归、分类
进一步成熟时间序列对齐模块
加入并贡献!
6.8 总结#
sktime- 用于时间序列学习的模块化框架面板数据 = 时间序列集合 - 任务包括分类、回归、聚类
使用 transformer 构建灵活的管道,通过网格搜索等进行调优
面板评估器通常依赖于时间序列距离、核、对齐器
时间序列距离、核、对齐器也可以通过模块化、灵活的方式构建
上述所有对象都是具有
sklearn类似接口的一等公民!
鸣谢:notebook 6 - 时间序列距离、核、对齐#
notebook 创建人:fkiraly
